Routes of drug administration are the path by which a drug is introduced into the body. Certain tablets are intended not to be swallowed when taken. These are the buccal and sublingual preparations.
Buccal tablet is placed and retained the buccal region that is, between the oral mucosa and the mandibular arch where it dissolves and is absorbed into circulation. These two areas, unlike other buccal regions (such as the hard palate, gingiva, or dorsal surface of the tongue), do not have keratinized epithelia, so they are more favorable for drug absorption.
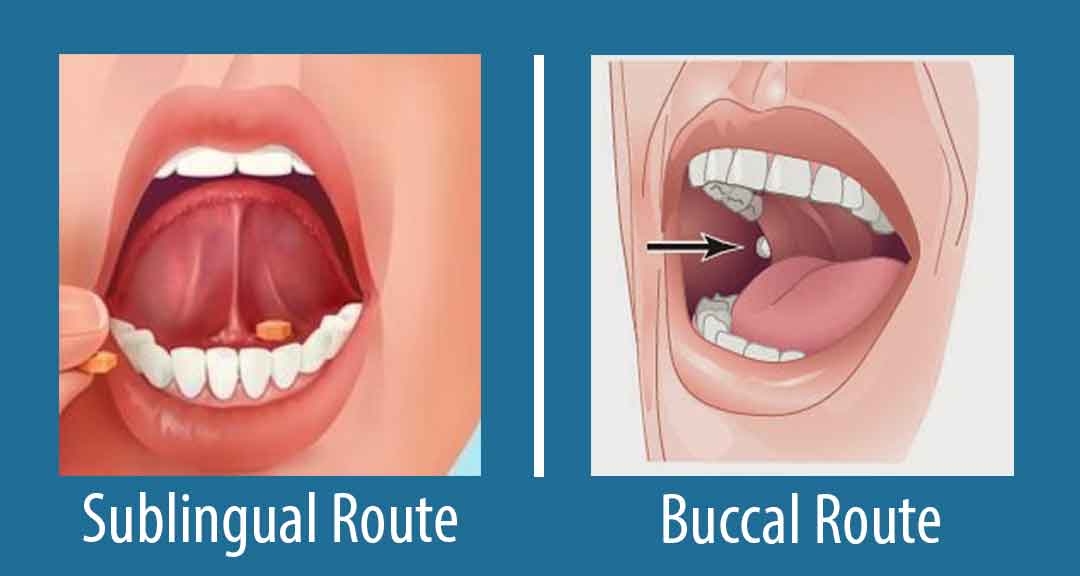
Sublingual preparations are placed and retained beneath the tongue where it dissolves and is absorbed into the circulation through the tissue there.
The main characteristic of buccal and sublingual routes of administration is the rapid onset of action (several minutes), which is due to the high blood flow and lymphatic flow of the oral cavity. In addition, substances absorbed at this level reach the general circulation without loss due to a first-pass effect, as the buccal venous drainage flows directly into the superior vena cava.
Read Also: Oral Administration of Drugs: Advantages and Disadvantages
Some advantages of administering drugs through the oral mucosa are:
1. A rapid onset of the therapeutic effect is achieved, not only by the high blood supply of the area but also by the lack of gastrointestinal (GI) factors that delay absorption (gastric emptying, presence of food, gastric disease, etc.).
2. Portal circulation is avoided, which allows to improve the bioavailability of a drug (regarding the oral route) avoiding intestinal and first-pass hepatic metabolism.
3. The active ingredient is not exposed to the aggressive GI medium, reason why it is possible the buccal administration of some drugs (e.g. peptides) that would otherwise be degraded by the GI pH or enzymes.
4. It can be done in patients with swallowing difficulties, nausea or malabsorption syndrome, and even in unconscious patients.
5. Action can be terminated by spitting out the tablet.
6. Self-administration is possible.
1. Due to the small size of the oral cavity, only very potent drugs can be effectively delivered. The buccal mucosa offers about 200 cm2 of area for drugs absorption, i.e. about 10,000 times less than duodenum.
2. Difficulty in keeping the drug in the site, as well as the need for the patient to refrain from swallowing, talking, or drinking during administration so as not to affect the residence time in which the medication is in direct contact with the mucous membrane.
3. Buccal and sublingual routes of administration are not applicable to bitter or bad-tasting drugs since, in addition to patient discomfort, this type of formulations generates excessive production of saliva, which increases the risk of swallowing.
4. While absorption may occur by any of paracellular and transcellular mechanisms studied, passive diffusion of drugs from the salivary aqueous phase through the membranes of oral mucosal cells predominates. Therefore, drugs of intermediate polarity are well absorbed, since excessive lipophilicity limits drug dissolution, in the same way that an increased polarity limits diffusion across cell membranes. The degree of ionization is also important: less ionized compounds at salivary pH are better absorbed.